
Seminar slides and workshop material will be made available on our GitHub page:
https://github.com/ImageAnalysis-RockefellerUniversity
Outline
- Segmentation
- Cell/particle Counting and Tracking
- Image denoising
Open-source Softwares
ImageJ/Fiji, QuPath, Napari, CellProfiler, Icy
Commercial Softwares
Imaris, Arivis, Aivia, Huygens, MetaMorph
Machine/Deep Learning frameworks
Weka, ilastik, Labkit StarDist, Cellpose, DeepImageJ, ZeroCostDL4Mic
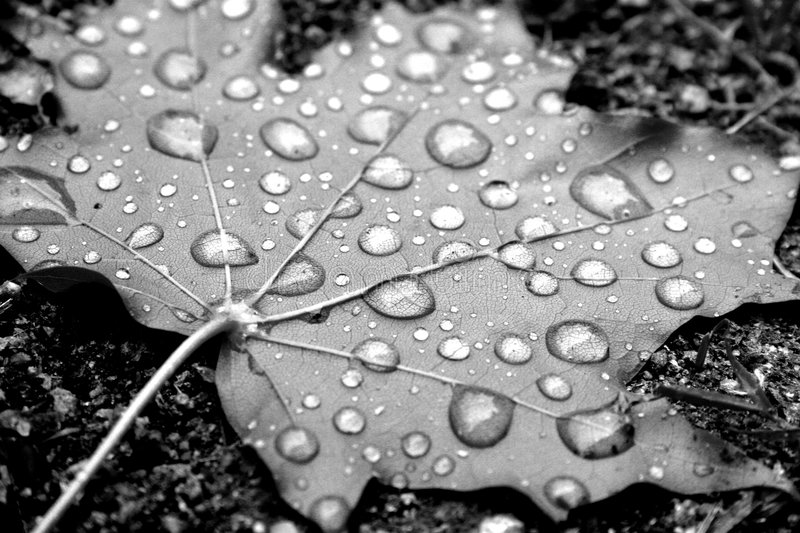
What is a Raster Image?
- Raster images are composed of a grid of pixels
- Each pixel contains intensity information
- Number of bits (N) determine the range of intensity levels
| Image Type | Range of intensity levels (0 to 2N-1) |
|---|---|
| 8-bit | 0-255 |
| 16-bit | 0-4095 |
| 32-bit | 0-65,535 |
| RGB color (3 x 8 bits) | 0-255 per channel |


Segmentation
Identifying object(s) of interest in an image
- cells, nuclei, membrane, transcription sites etc.
Segmentation is usually followed by quantitative analysis of object(s)
- number of cells/nuclei, mean fluorescence intensity, shape etc.
Divide image into areas representing object(s) of interest and background
Segmentation is not an easy task to solve in most practical cases
- Signal variability throughout the image
- Noise, blur and other distortions caused by the imperfect imaging conditions
Segmentation tools
- Global thresholding, local thresholding
- Image processing filters – Gaussian, Median, Sobel etc.
- Machine learning methods (supervised learning) - Weka, Labkit, ilastik
- Deep Learning methods - StarDist, Cellpose
- 3D segmentation - Imaris, Arivis
Segmentation using global thresholding
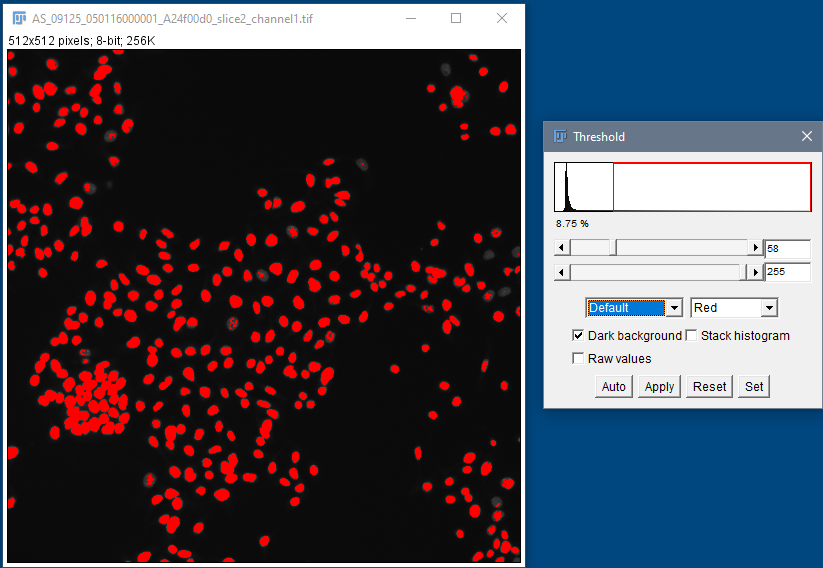
Human HT29 colon cancer cells, Image from Broad Bioimage Benchmark Collection, Ljosa et al. 2012 Nat Methods
Segmentation using global thresholding

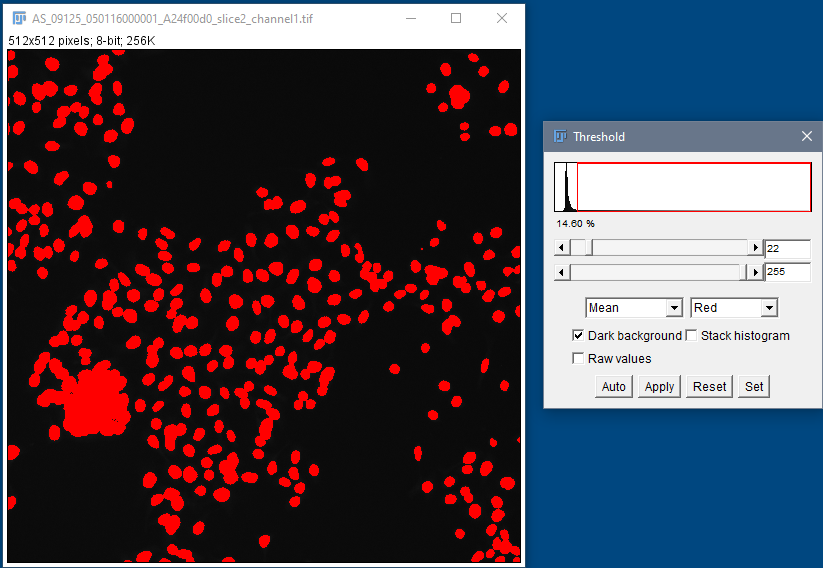
Human HT29 colon cancer cells, Image from Broad Bioimage Benchmark Collection, Ljosa et al. 2012 Nat Methods
Segmentation with local thresholding

Auto Local
Threshold
in Fiji
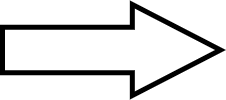
Human HT29 colon cancer cells, Image from Broad
Bioimage Benchmark Collection, Ljosa et al. 2012 Nat Methods
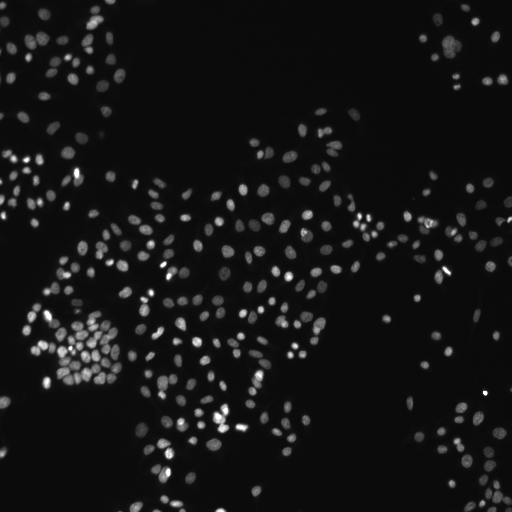
Segmentation using Machine Learning
Supervised learning - pixel classification using Random Forest classifier
Fiji (Weka and Labkit plugins), ilastik, QuPath, Napari, CellProfiler
Requires orders of magnitude less training data/resources than Deep Learning methods
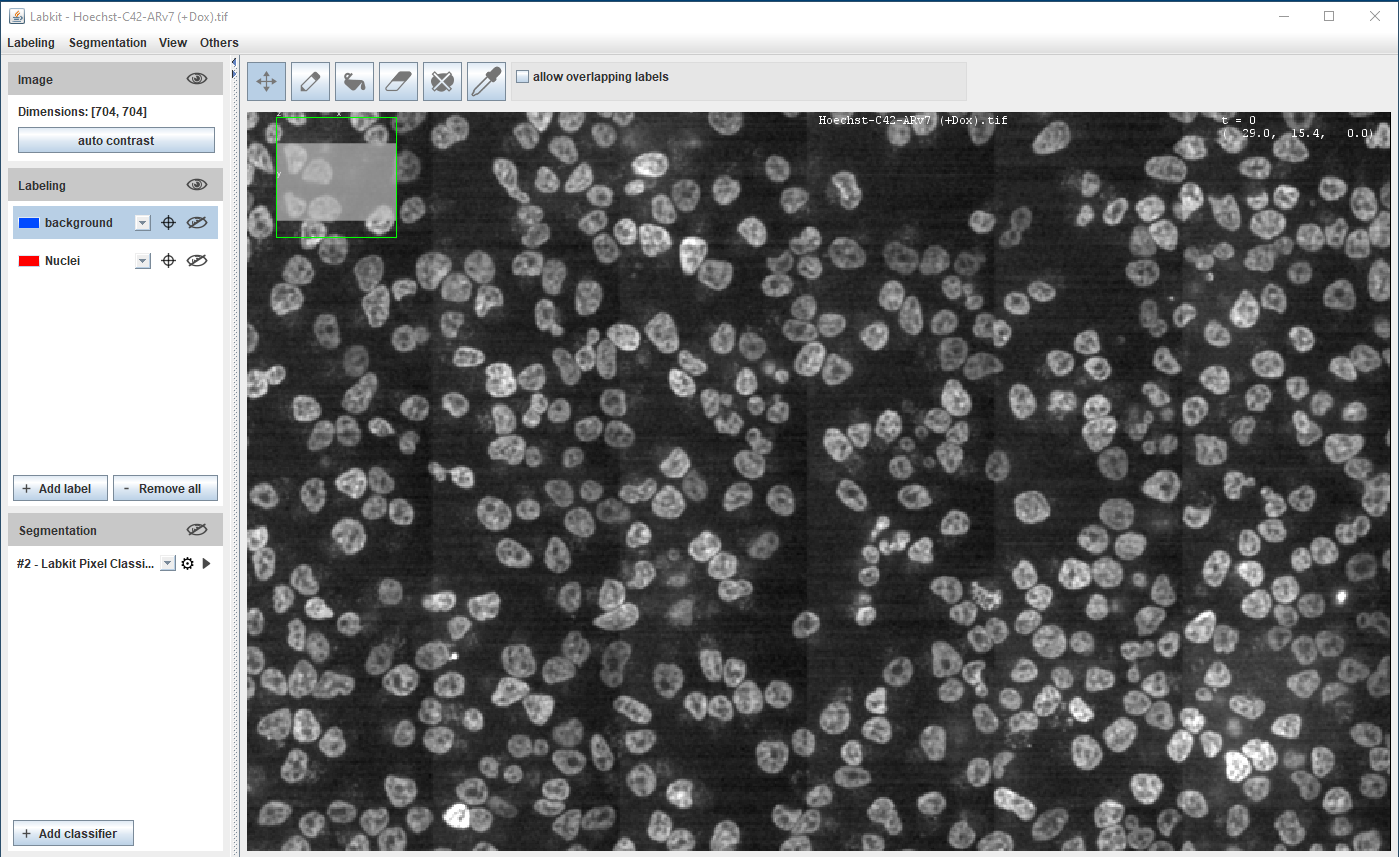
Hoechst-stained Nuclei, image courtesy of Cherie Au, Giannakakou Lab, Weill Cornell Medicine
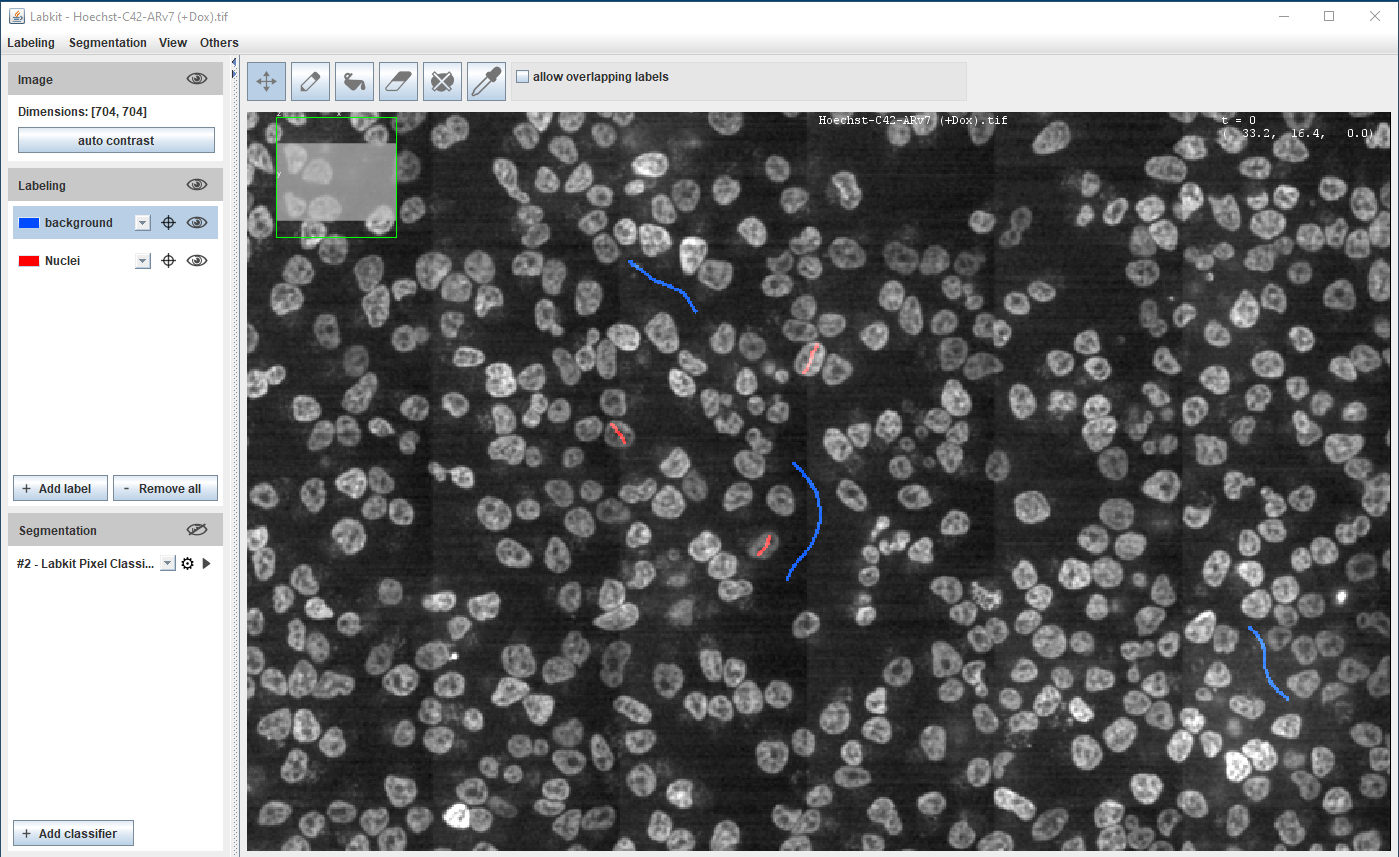
Hoechst-stained Nuclei, image courtesy of Cherie Au, Giannakakou Lab, Weill Cornell Medicine
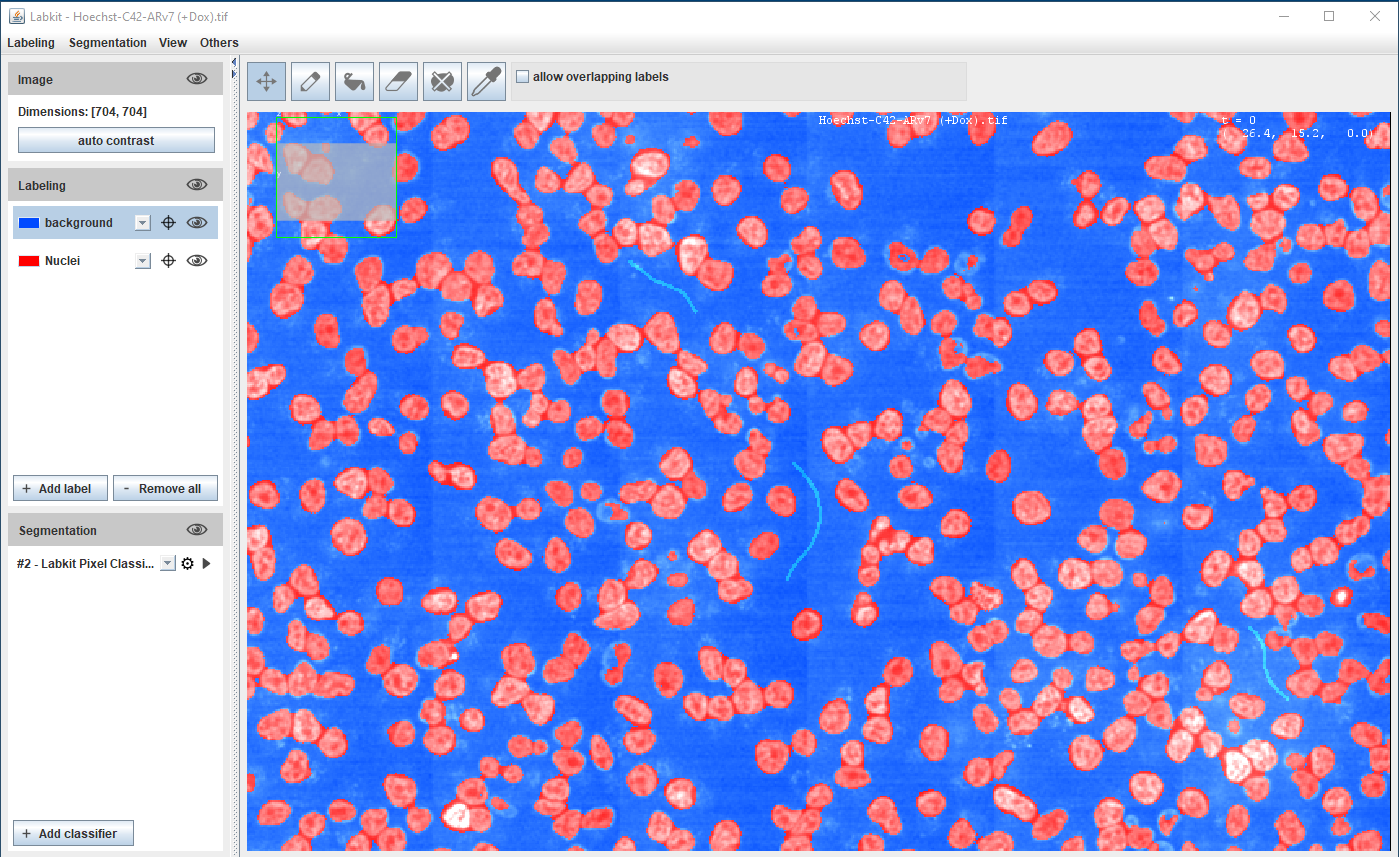
Hoechst-stained Nuclei, image courtesy of Cherie Au, Giannakakou Lab, Weill Cornell Medicine
Segmentation using Deep Learning
Most accurate methods available for cells/nuclei segmentation
Step 1: Training
Generating a Deep Learning model is resource hungry:
- High-end workstation
- Large amounts of training data (images and annotations)
- Training could take hours to days
- Good programming knowledge required - Python
Step 2: Prediction
Using the model from step 1 to predict the segmentation results :
- A regular laptop is just fine
- Prediction takes seconds to mins
- Little to no programming knowledge required


Segmentation using Deep Learning
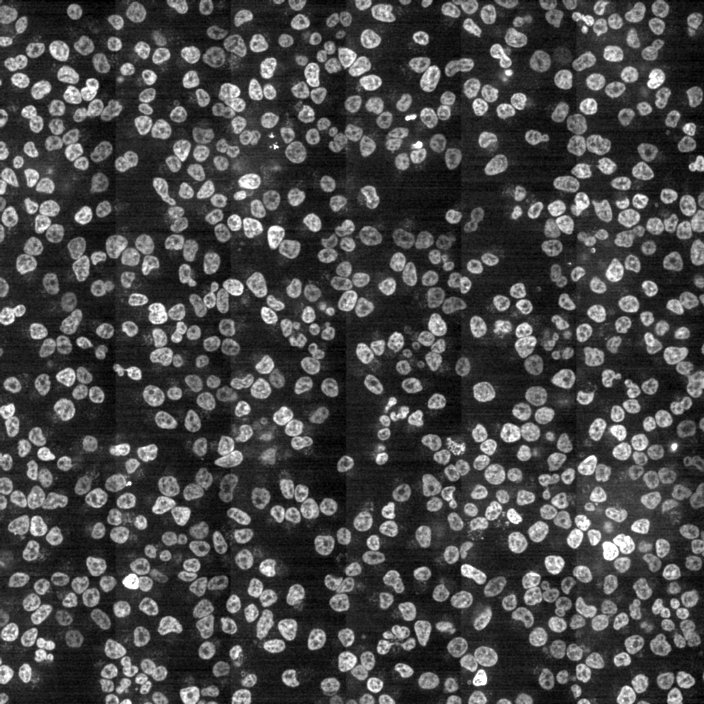
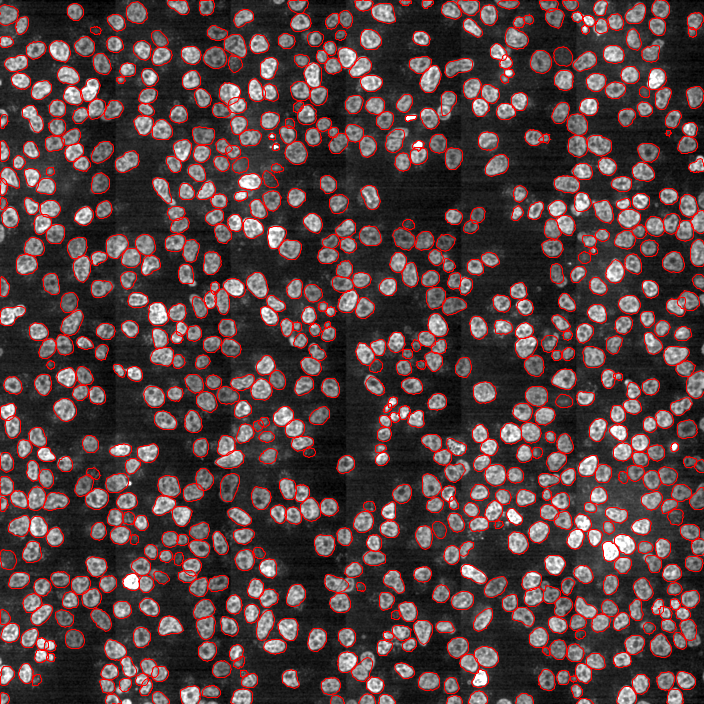
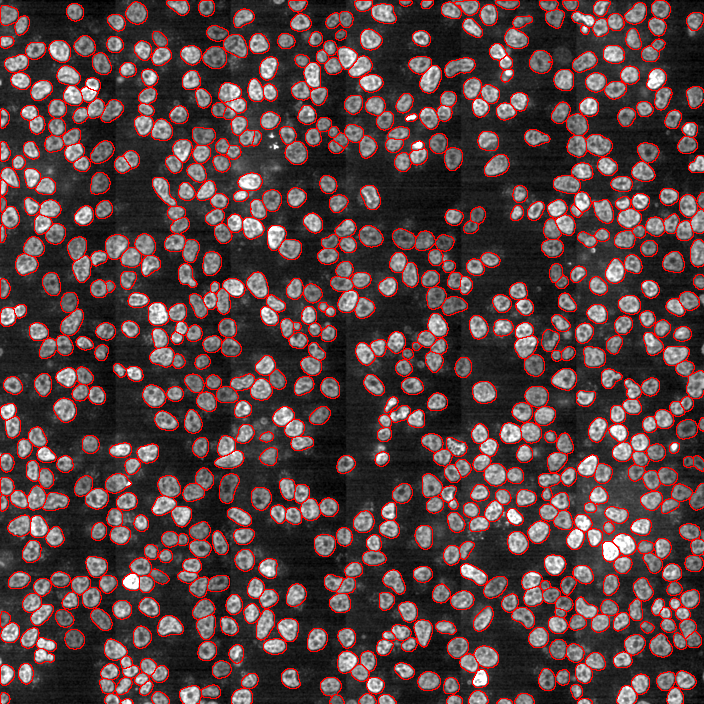
Hoechst-stained Nuclei, image courtesy of Cherie Au, Giannakakou Lab, Weill Cornell Medicine
Workshop Exercise 1: StarDist based nuclear segmenation in a challenging image in Fiji
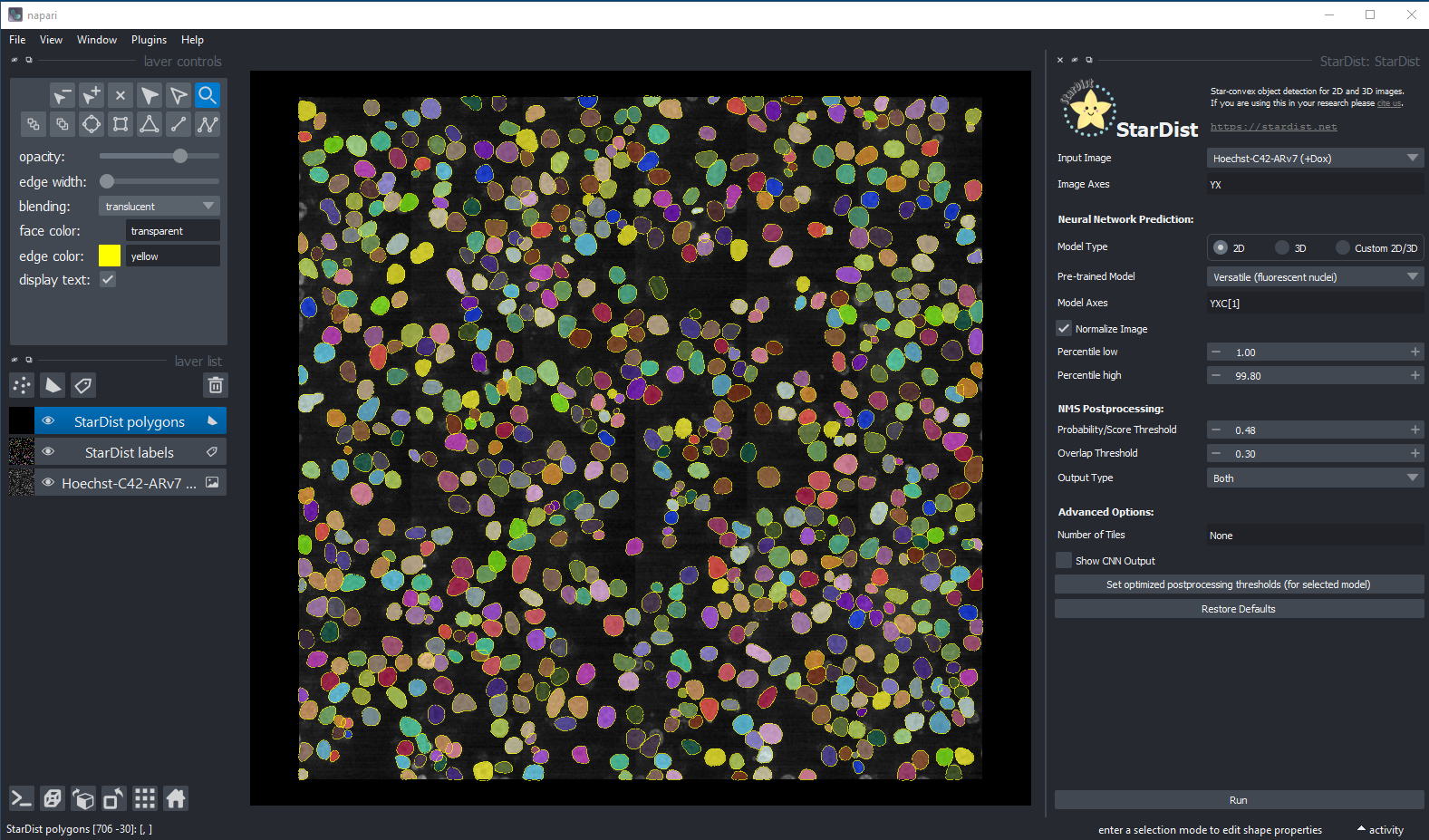
Segmentation using StarDist in Napari
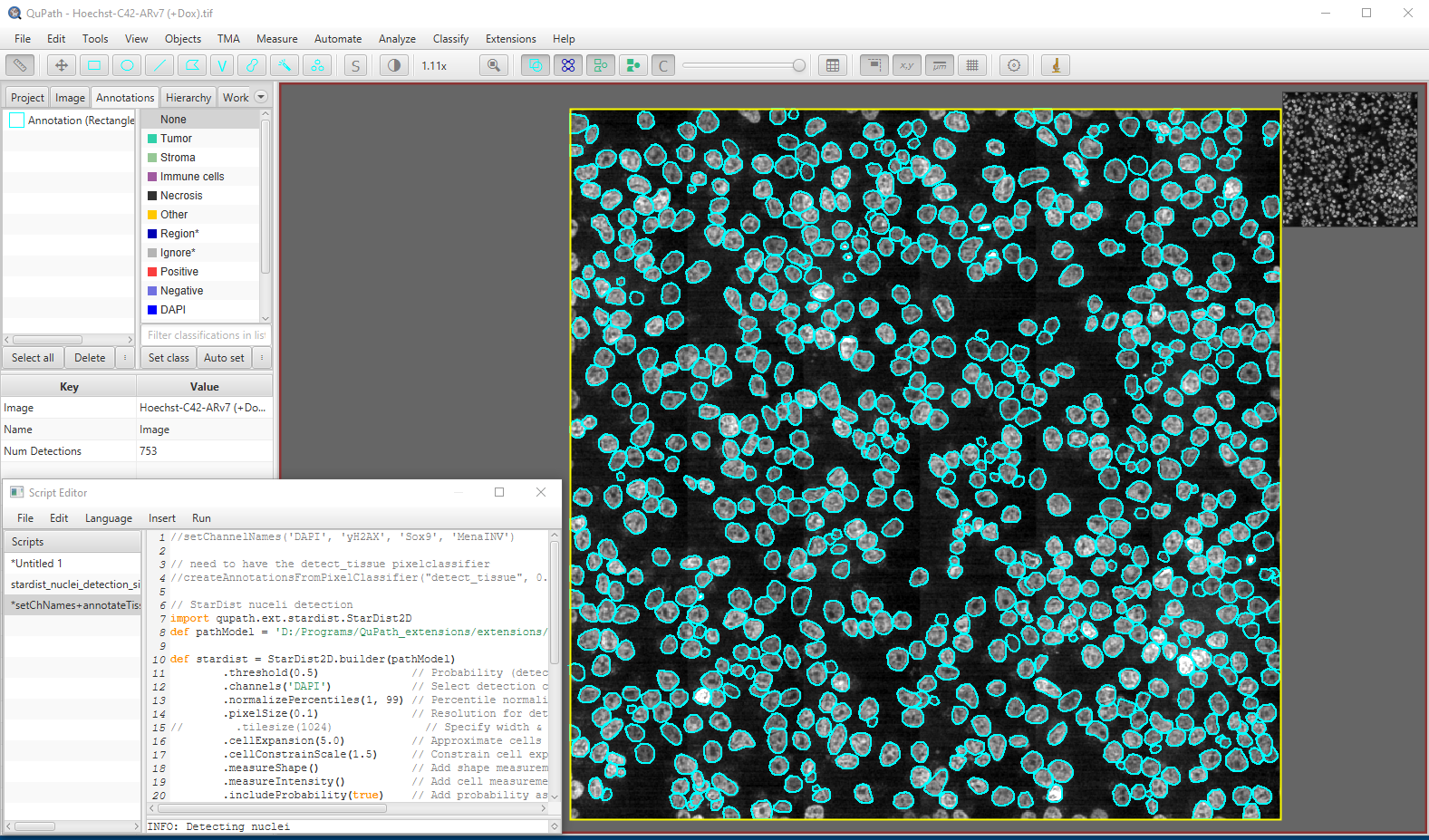
Segmentation using StarDist in Qupath
Segmentation – comparison of Deep Learning models
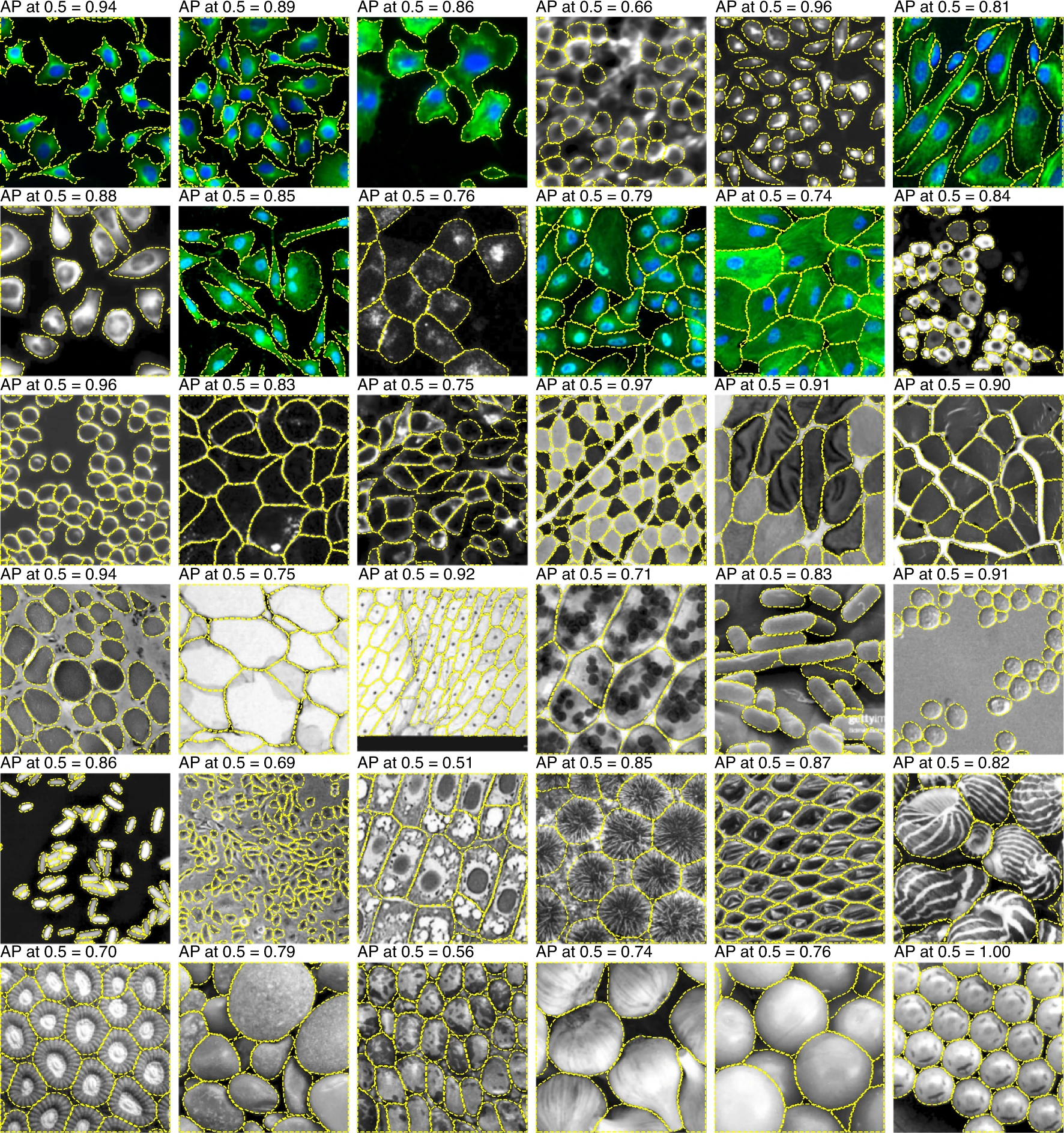
Cellpose
Stringer et al 2021, Nat Methods
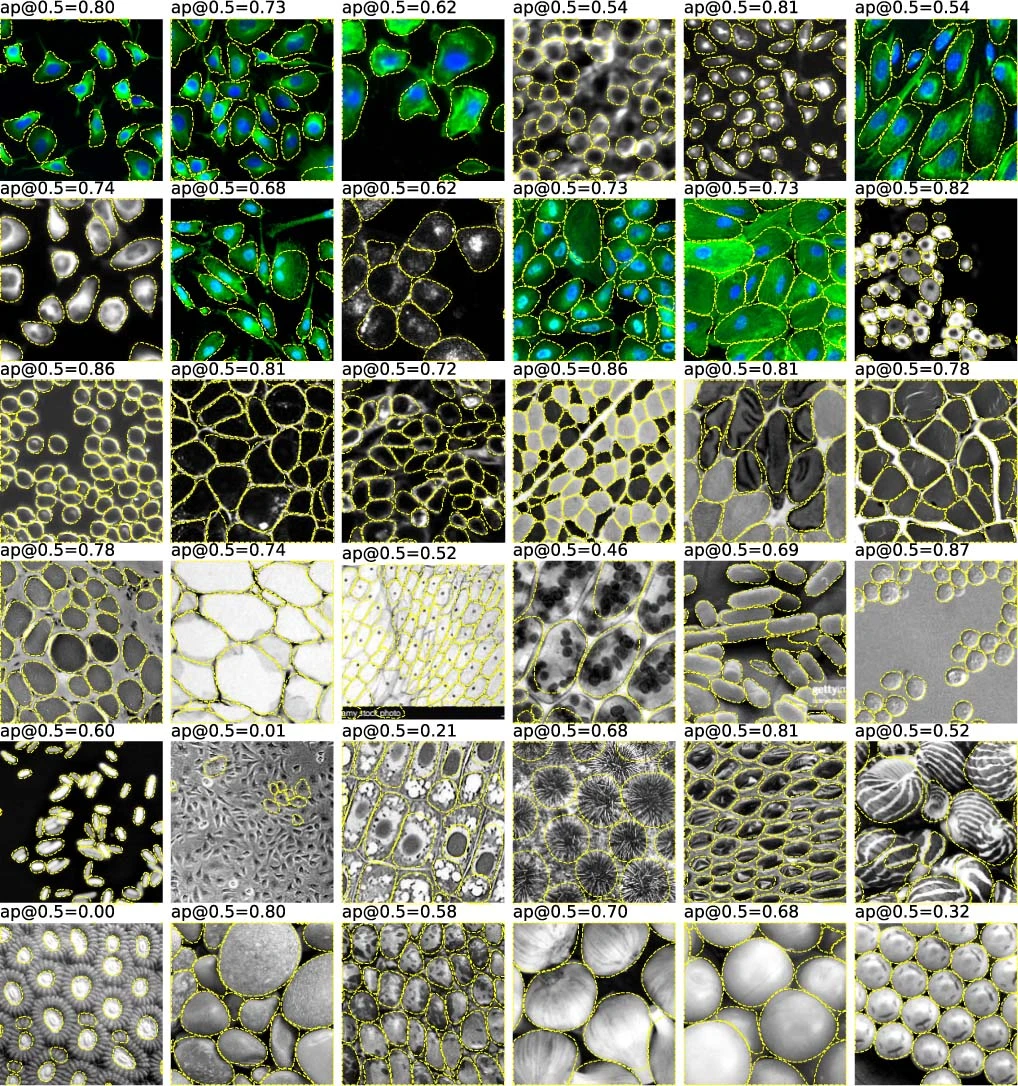
StarDist
Stringer et al 2021, Nat Methods
Challenging cases
1. Cell crowding
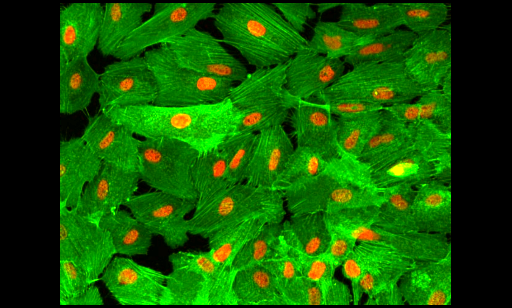
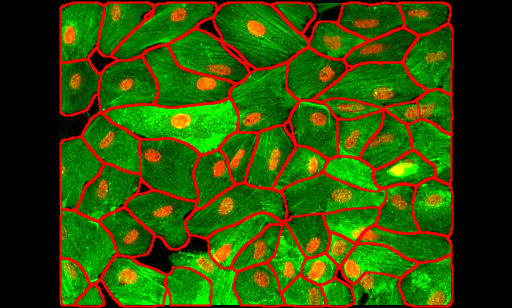
Image from https://github.com/MouseLand/cellpose
2. Cell crowding + noisy signal
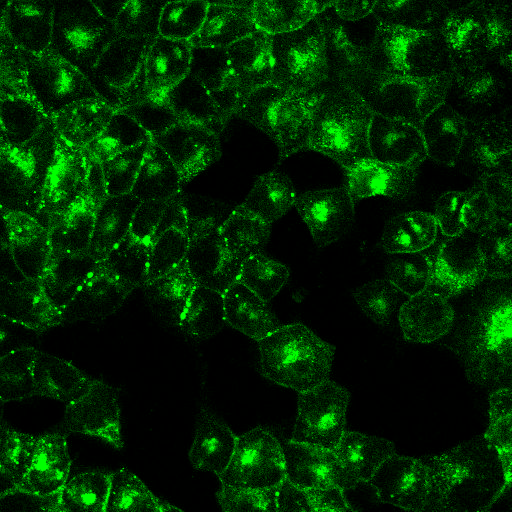
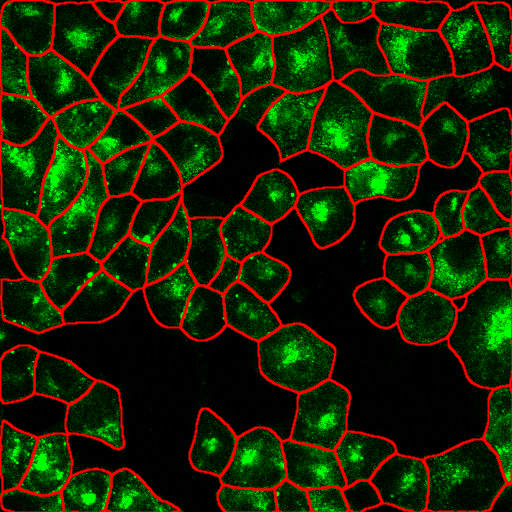
Image from https://github.com/MouseLand/cellpose
3. Cell crowding + uneven illumination
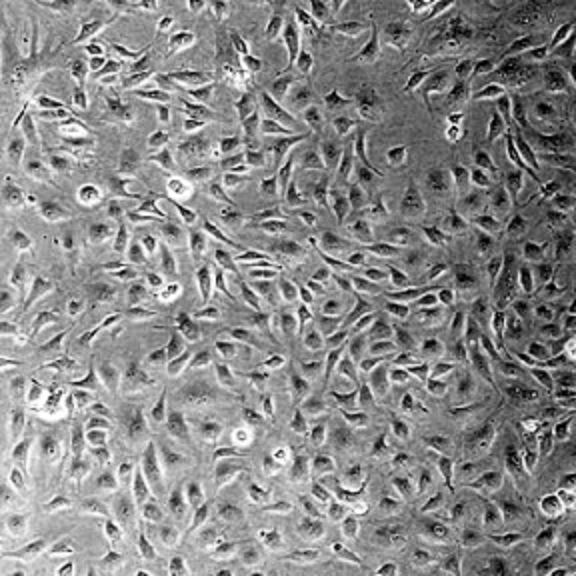
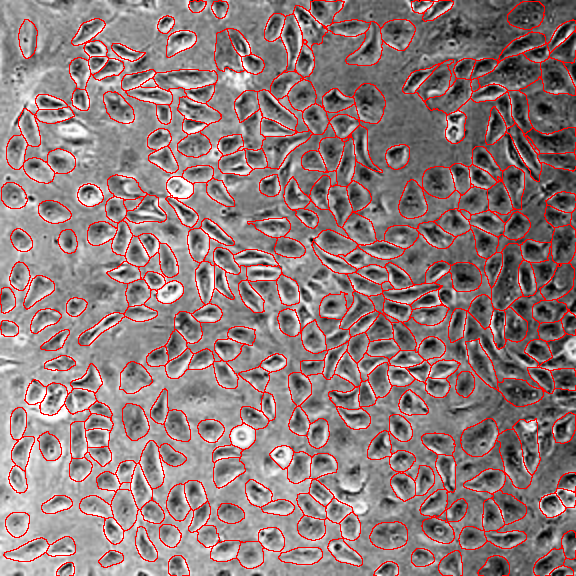
Image from https://github.com/MouseLand/cellpose
Bio-Imaging Resource Center, The Rockefeller University